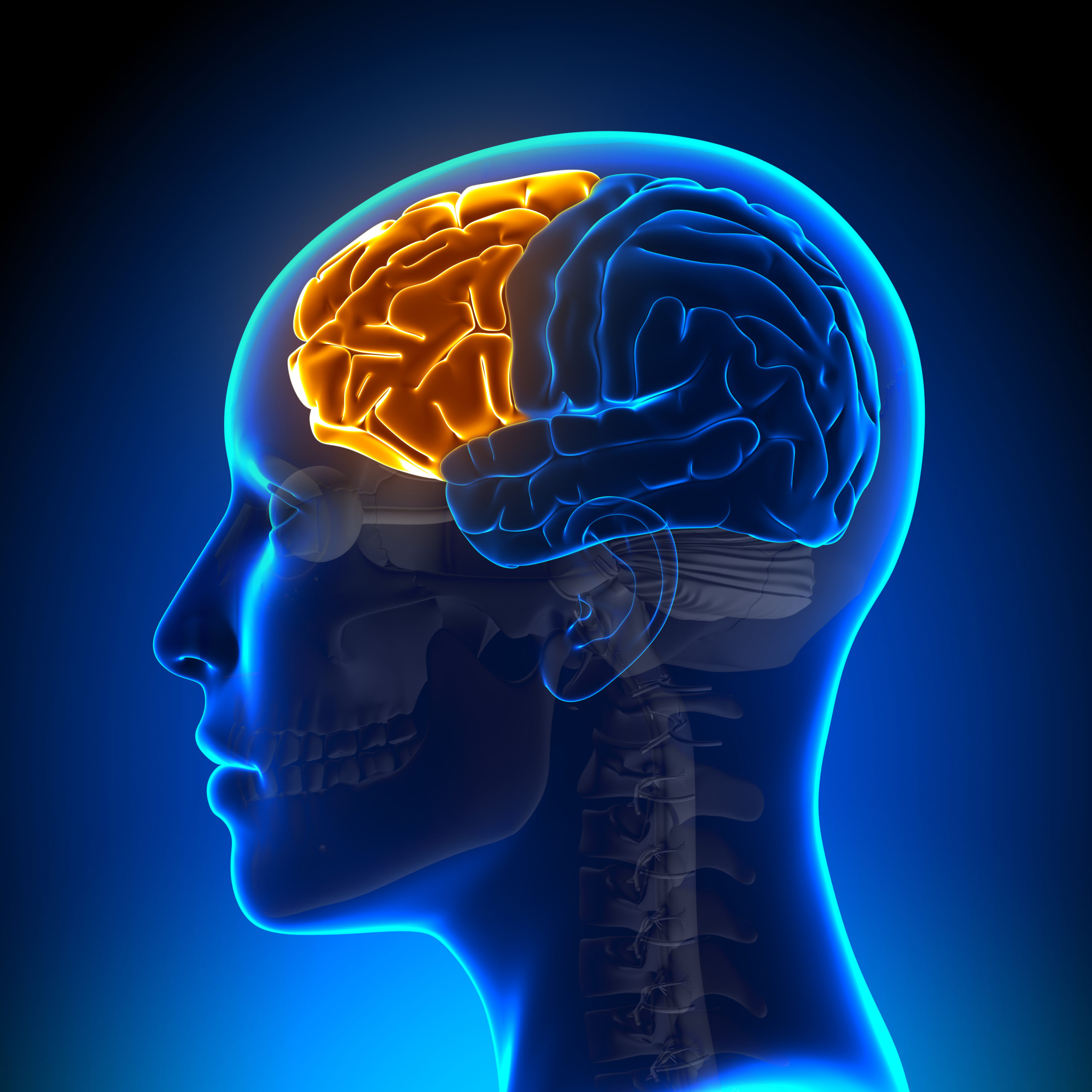
When the brain sustains sudden damage, it is referred to as a traumatic brain injury (TBI). The American Association of Neurological Surgery explains that TBI “is a disruption in the normal functioning of the brain that can be caused by a blow, bump or jolt to the head, the head suddenly and violently hitting an object or when an object pierces the skull and enters brain tissue.” The specific symptoms that develop because of a TBI will vary significantly, as they depend on the type of injury, the severity of the injury, as well as the area of the brain that was injured. The brain is divided into two hemispheres which are called the right hemisphere and the left hemisphere. Each hemisphere has a set of four lobes, which are in specific areas of the brain and are each associated with a set of functions, as indicated below:
- Frontal lobe: located in the front section of the brain, is important for cognitive functions and control of voluntary movement or activity
- Parietal lobe: located in the center section of the brain, processes information about temperature, taste, touch, and movement
- Temporal lobe: located in the side section of the brain, processes memories, integrating them with sensations of taste, sound, sight, and touch
- Occipital lobe: located in the back section of the brain is primarily responsible for vision
Damage to the frontal lobe can lead to a variety of potential symptoms, including but not limited to the following examples provided by Healthline:
- Loss of movement, either partial (paresis) or complete (paralysis), on the opposite side of the body
- Difficulty performing tasks that require a sequence of movements
- Trouble with speech or language (aphasia)
- Poor planning or organization
- Persistence with one behavior, way of thinking, or set of rules
- Difficulties with higher order functions like reasoning, problem-solving, and judgment
- Problems with maintaining attention or concentration
- Decreased motivation
- Mood swings
- Impaired ability to initiate activities or interactions
- Drastic changes in personality or behavior, which can include apathy, irritability, and inappropriate social behavior
- Poor impulse control or lack of inhibition
It is important to note that for some individuals, a TBI may only affect the exact location on the brain where the injury occurred, while for others a TBI could also affect surrounding tissues and cause damage to one’s brain in other areas, apart from the initial site.
For Information and Support
If you are concerned for yourself or a loved one regarding substance abuse and/ or addiction, we recommend reaching out for help as soon as possible. If left untreated, substance abuse can result in long-lasting and potentially life-threatening consequences. Keep in mind: you are not alone! There is an entire network of professionals that are available to help and support you and your loved one throughout the recovery process. The earlier you seek support, the sooner your loved one can return to a happy, healthy, and fulfilling life.
Please do not hesitate to reach out with any questions regarding our specific program at Haven House Addiction Treatment and/ or general substance abuse and/ or addiction treatment-related information. Our highly trained staff is readily available to discuss how we might best be able to help you and your loved one. We can be reached by phone at 424-258-6792. You are also welcome to contact anytime us via email at admissions@hhtxc.com.