Sober Living in Los Angeles, California
Haven House Sober Living is your partner in the journey toward recovery from substance abuse in sunny Los Angeles, California.
At Haven House, we believe in providing a caring and supportive environment where individuals can rebuild their lives and embrace long-lasting sobriety with the help of our experienced team and recovery program.
 Discover Our Sober Living Home
Discover Our Sober Living Home
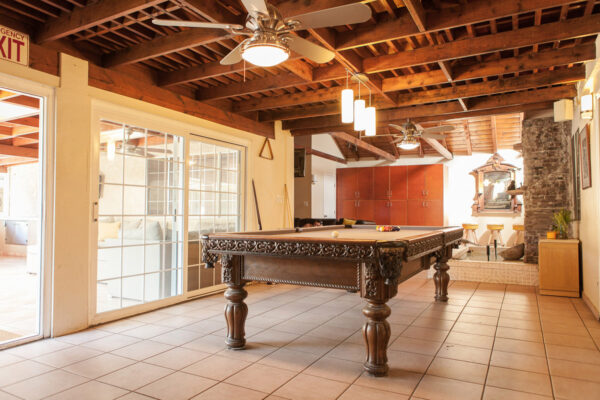
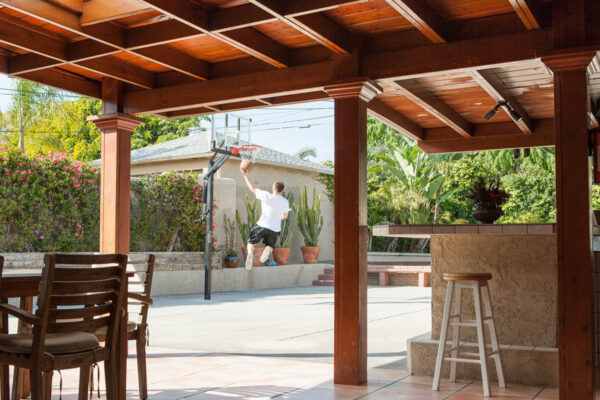
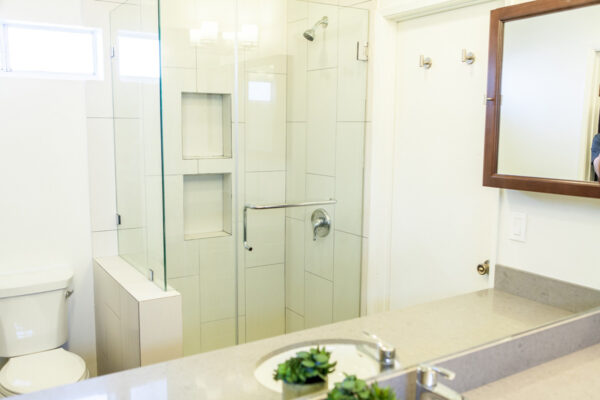
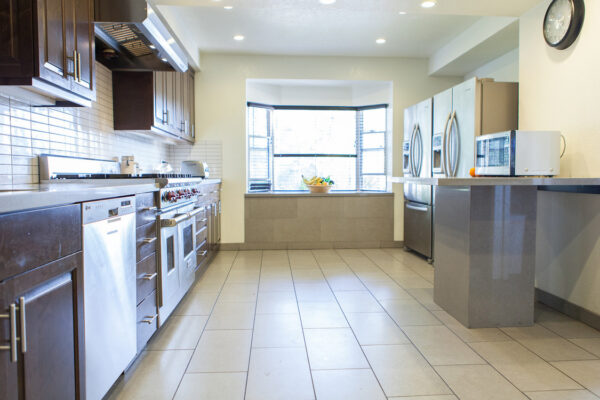
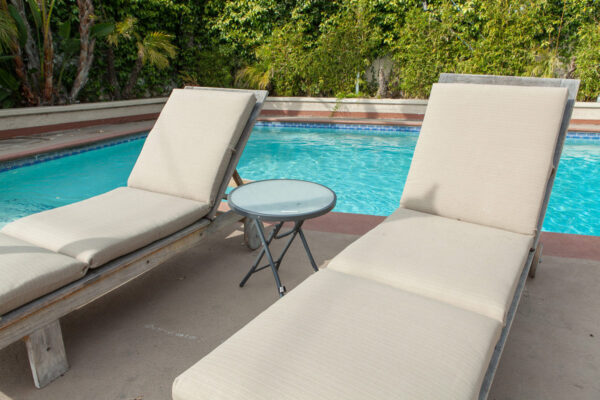
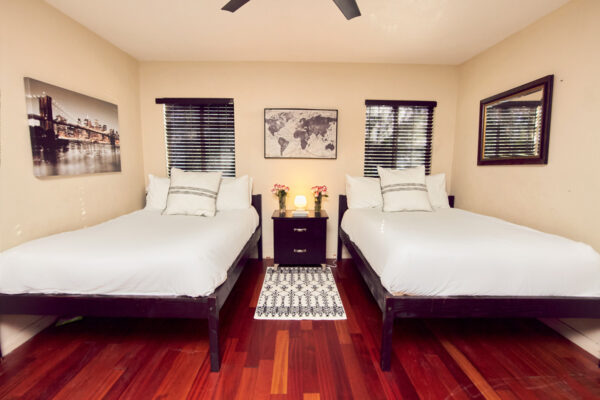
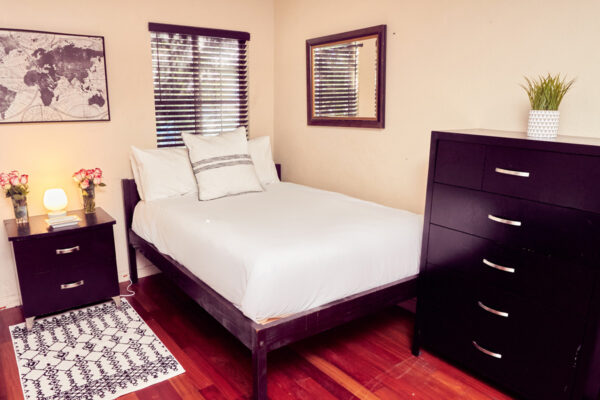
Nestled in the heart of Los Angeles, our sober living home offers more than just a place to stay — it offers a path to a new beginning. Our luxury sober living facility provides a serene oasis for individuals on their quest for long-term recovery.
Luxury Accommodations: Our upscale sober living house is meticulously designed to provide comfort and tranquility, setting the perfect stage for healing and growth.
Pet-Friendly Environment: We understand the importance of companionship during recovery, so our facility welcomes furry friends to offer additional emotional support.
 Our Comprehensive Services
Our Comprehensive Services
At Haven House Sober Living, we offer a comprehensive range of tailored services to support individuals at every stage of their addiction recovery journey. Our goal is to provide a nurturing environment that fosters mental health, overall wellness, and the development of essential life skills for long-term sobriety.
Safe Haven

Our sober living program offers a safe haven for those recovering from substance abuse. Find support from peers to continue your path to sobriety with ease.
Life Skills Mentoring

We believe in empowering individuals with the tools necessary to navigate the challenges of independent living through individualized life skills mentoring and guidance.
 Supportive Environment for Long-Term Recovery
Supportive Environment for Long-Term Recovery
At Haven House, we are committed to providing a supportive and compassionate environment that encourages individuals to overcome their addiction and embrace a new life free from active substance abuse. Our dedicated staff members are here to guide residents through their recovery journey with care and understanding.
Caring Staff Members
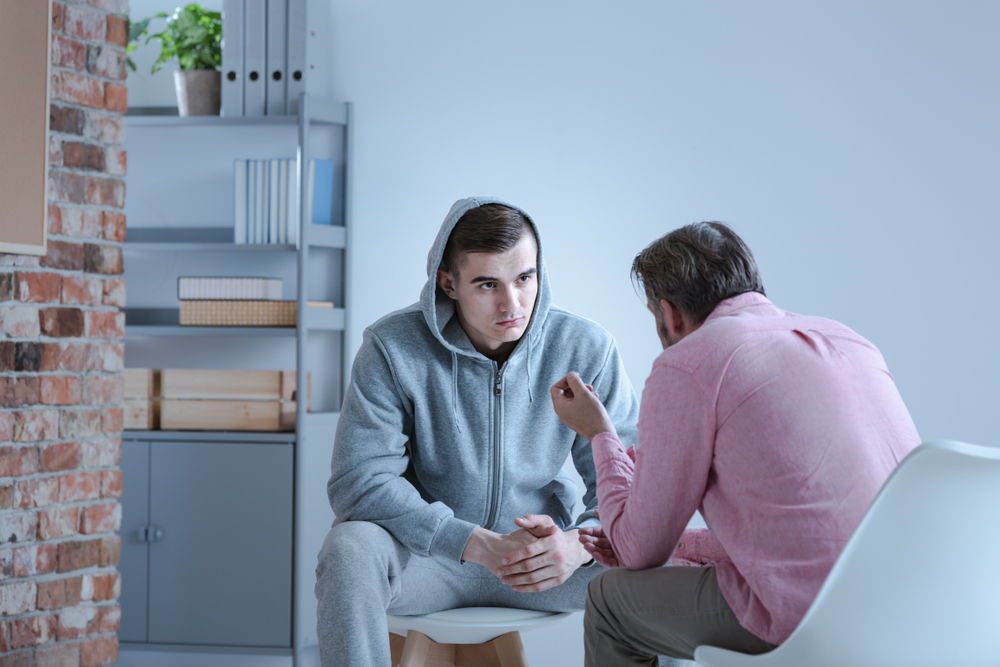

Our team consists of compassionate and experienced professionals dedicated to ensuring each resident’s well-being and progress, offering support and encouragement every step of the way.
Accountability and Progress
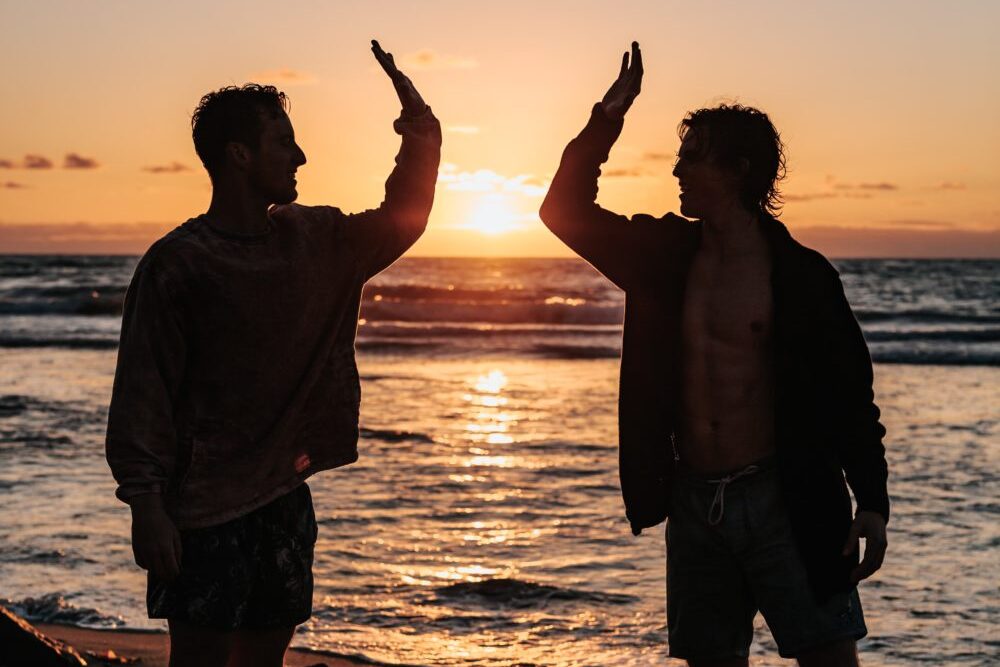

We instill a sense of accountability and progress through regular drug testing and relapse prevention strategies, helping residents stay focused on their sober living program and recovery goals.
Culture of Recovery
Haven House fosters a culture of recovery that promotes self-care, personal growth, and community engagement, creating a safe and empowering space for individuals to thrive.
Join us at Haven House Sober Living and begin a journey toward long-term sobriety and wellness in a supportive and welcoming environment tailored to your needs.
Sober Living Gallery
 Embracing New Beginnings
Embracing New Beginnings
At Haven House Sober Living, we believe in the transformative power of embracing new beginnings. Our program is designed to help individuals transition into a new life, providing a supportive and encouraging environment where growth, empowerment, and hope flourish
Hope and Empowerment
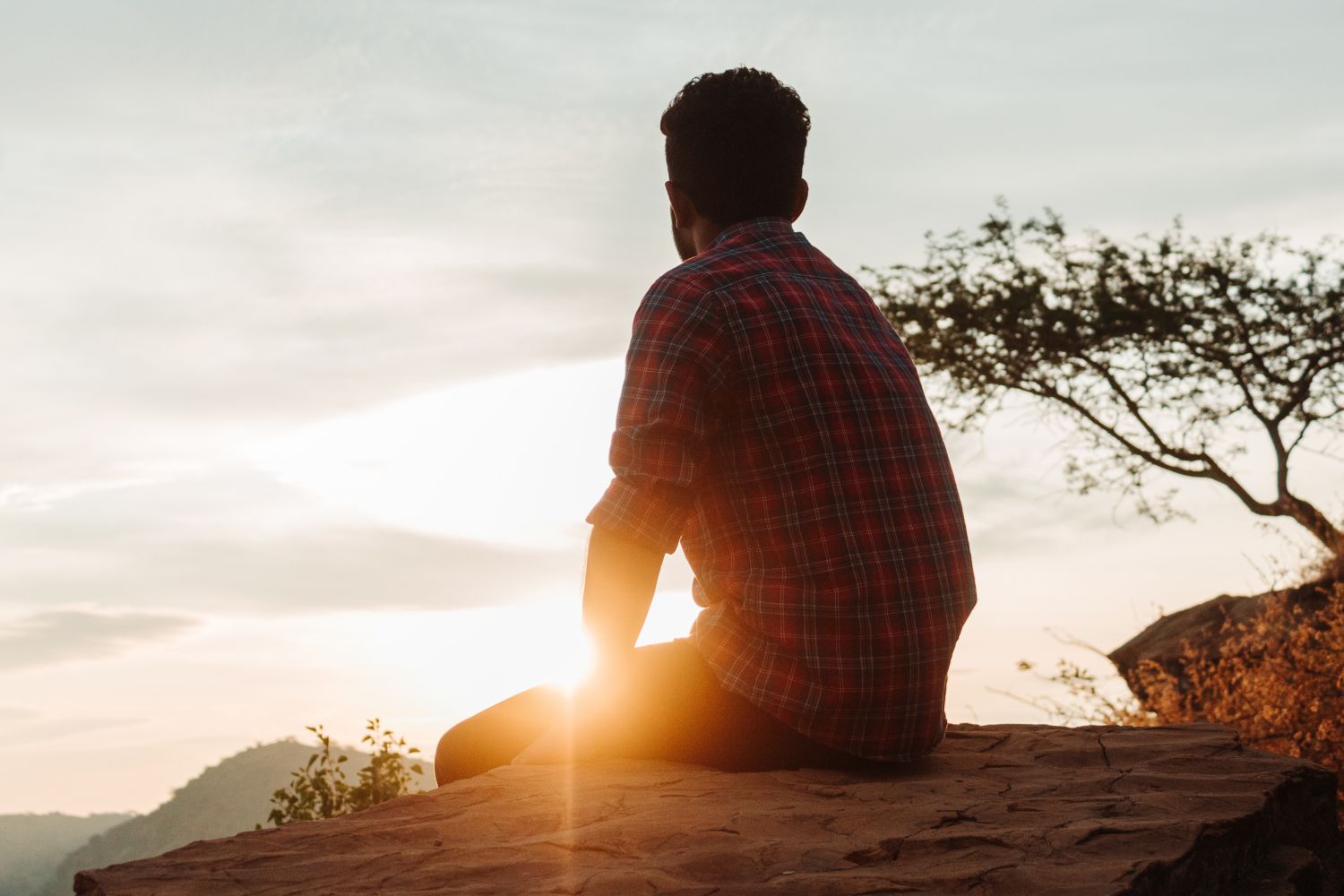

We promote a sense of hope and empowerment in our residents, guiding them toward a future free from active addiction and filled with new opportunities for personal development
Success Stories
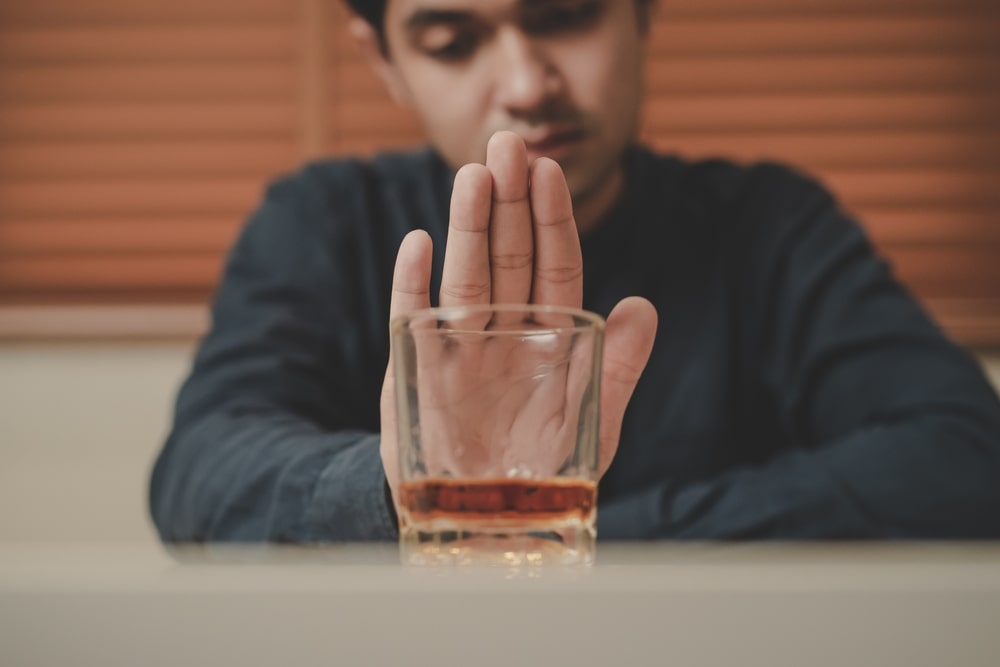

Hear from individuals who have found success in our program through testimonials that showcase the positive impact of our supportive community and personalized approach to recovery.
 Engaging with the Recovery Community
Engaging with the Recovery Community
Joining the vibrant recovery community in Los Angeles is integral to the Haven House Sober Living experience. We connect residents with local 12-step meetings and other resources to create a supportive network that enhances the recovery journey.
Holistic Support: We offer holistic support by fostering collaboration with local recovery resources, encouraging individuals to actively engage with the recovery community for sustained progress and well-being.
Family Involvement: Family members are encouraged to be part of the recovery process, with resources available to support their involvement and understanding of their loved one‘s journey to sobriety.
Experience the transformative power of community and connection at Haven House Sober Living, where each individual is guided toward recovery and wellness in a caring and inclusive environment.
Ensuring Accountability and Progress
At Haven House Sober Living, we prioritize accountability and progress as key components of the recovery journey. We offer comprehensive measures to ensure residents stay on track toward their sobriety goals and continue making positive strides in their personal growth and well-being.
Regular Drug Testing: Our program includes regular drug testing to help individuals stay accountable and maintain a sober lifestyle, fostering a sense of responsibility and commitment to their recovery.
Relapse Prevention Strategies: Through personalized relapse prevention strategies, residents learn valuable techniques and coping skills to navigate triggers and challenges, empowering them to prevent relapse and stay focused on their long-term recovery goals.
Moving Toward Long-Term Sobriety
Haven House Sober Living is dedicated to supporting individuals in building the foundation for long-term sobriety and embracing a fulfilling life free from substance abuse. Our program focuses on instilling values of self-care, personal growth, and resilience to empower residents as they move toward a brighter and healthier future.
Personalized Care: We provide personalized care and individualized attention to cater to the diverse needs of our residents, ensuring that each individual receives the support and guidance necessary for their unique journey to sobriety.
Empowering Individuals: Through a holistic approach that integrates physical, emotional, and mental well-being, we empower residents to take charge of their recovery process and make positive strides toward a life of sobriety and wellness.
Commitment to Success: Haven House Sober Living is committed to the success and well-being of each resident, fostering a culture of support, encouragement, and empowerment to facilitate long-term recovery and sustained sobriety.
Join us at Haven House Sober Living as we embark on a shared journey toward long-term sobriety, well-being, and a brighter future filled with hope, growth, and transformation in a supportive, nurturing community.
 Join the Haven House Family
Join the Haven House Family
Take the first step toward a new life of sobriety and well-being by joining the Haven House family. Our doors are open to individuals seeking a supportive and empowering environment to navigate their recovery journey with care and compassion.
Admission Process: Learn more about our admission procedures and amenities available at Haven House Sober Living as you begin this transformative experience toward long-term recovery.
Tour Our Facility: Schedule a tour of our luxury sober living home in Los Angeles to experience firsthand the serene and inclusive atmosphere that sets the stage for growth, healing, and new beginnings.
Engage with Us: Explore the possibility of becoming part of our supportive community at Haven House Sober Living in Los Angeles by contacting us for inquiries, questions, or further information.
Testimonials
Contact Us
Someone is standing by to help right now. Contact us anytime.
Mens Sober Living Beverlywood
2260 Hillsboro Avenue
Los Angeles, CA 90034






